
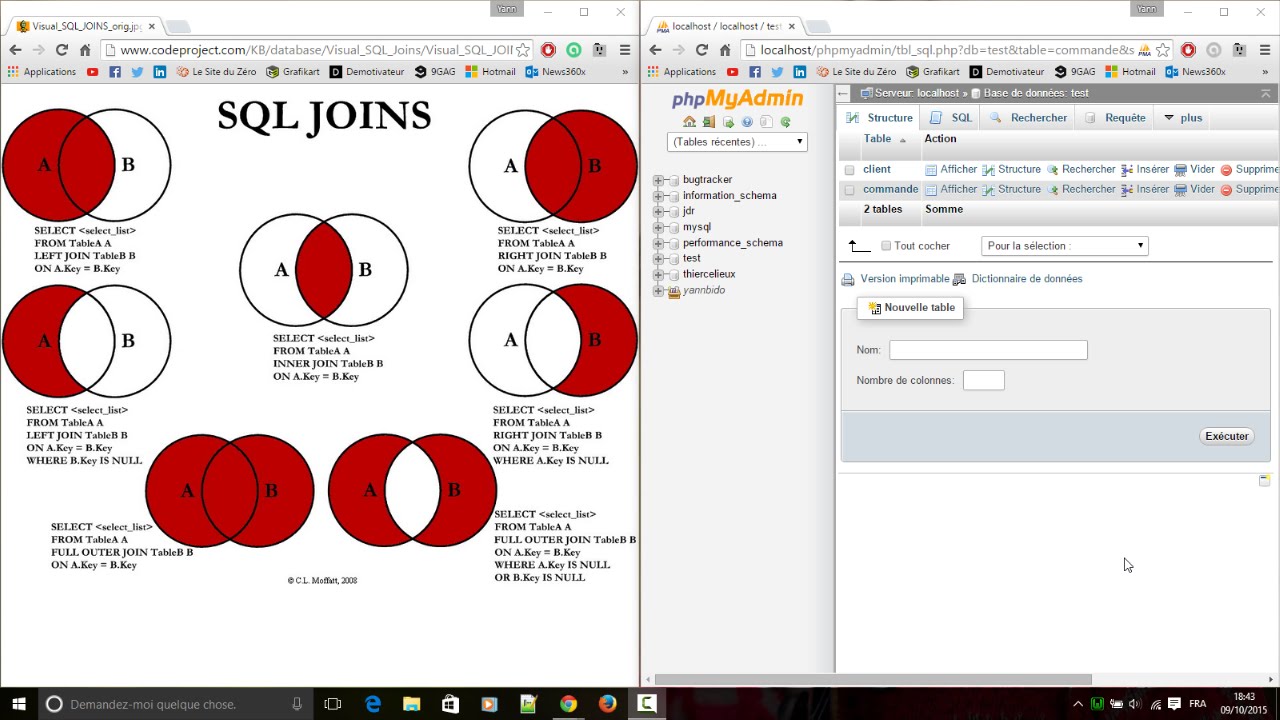
In this case, the columns from the left table return NULL values.Īn STRAIGHT_JOIN is such a join which scans and combines matching rows ( if specified any condition) which are stored in associated tables other wise it behaves like an INNER JOIN or JOIN of without any condition.Ī CROSS JOIN is such a join which specifies the complete cross product of two tables. The RIGHT JOIN is such a join which specifies that all records be fetched from the table on the right side of the join statement, even if the table on the left has no matching record. If a record returned from the left table has no matching record in the table on the right side of the join, it is still returned, and the corresponding column from the right table returns a NULL value. The LEFT JOIN is such a join which specifies that all records be fetched from the table on the left side of the join statement. An INNER JOIN allows rows from either table to appear in the result if and only if both tables meet the conditions specified in the ON clause. The INNER JOIN is such a JOIN in which all rows can be selected from both participating tables as long as there is a match between the columns. Here is the sample tables table_A and table_B, which we have used to explain the technologies behind the joins. | table_reference STRAIGHT_JOIN table_factor ON conditional_expr | table_reference STRAIGHT_JOIN table_factor
#Mysql join update
MySQL supports the following JOIN syntaxes for the table_references (A table reference is also known as a join expression.) part of SELECT statements and multiple-table UPDATE and DELETE statements : table_references:Įscaped_table_reference.
#Mysql join series
It is a good practice to think of the query as a series of two table joins when the involvement of three or more tables in joins. It can be difficult when the join involving more than two tables. The join can be performed as long as the data in the columns are matching.
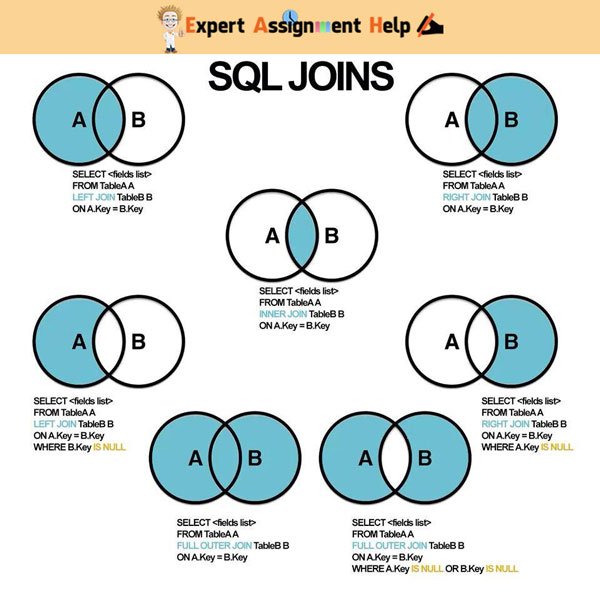
Mostly but not all of the time, the join key is the primary key of one table and a foreign key in another table. These columns, or possibly a single column from each table, are called the join key or common key. These values are usually the same column name and datatype that appear in both the participating tables being joined. JOIN clauses are used to return the rows of two or more queries using two or more tables that shares a meaningful relationship based on a common set of values. A join enables you to retrieve records from two (or more) logically related tables in a single result set.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
